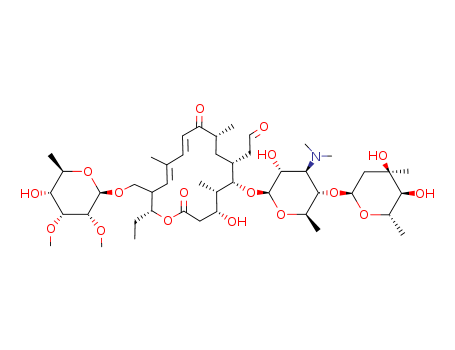

CasNo: 1401-69-0
MF: C46H77NO17
Appearance: COA
|
Indications |
In cattle, tylosin is used for treatment of BRD caused by Mannheimia, Pasteurella multocida, and Histophilus somni (formerly Haemophilus somnus). It is used for interdigital necrobacillosis (foot rot) in cattle caused by Fusobacterium necrophorum or Bacteroides melaninogenicus. In pigs, it is used for treatment of swine arthritis caused by Mycoplasma hyosynoviae, swine pneumonia caused by Pasteurella spp., swine erysipelas caused by Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae, swine dysentery associated with Serpulina (Treponema) hyodysenteriae, and proliferative enteropathy caused by L. intracellularis. For treatment in pigs, it is also added to feed (Type A–medicated feed article) or drinking water. In small animals, it is used for gram-positive soft tissue and skin infections. However, the most common use in dogs is for treatment of diarrhea, referred to as antibiotic-responsive diarrhea, that has not responded to other treatments. The etiology of the diarrhea is not known but may be caused by Clostridium or Camphylobacter. For this use, the powdered formulation (swine formulation) is most often added to food daily for maintenance. |
|
Contact allergens |
Tylosin is a macrolid antibiotic used in veterinary medicine. Occupational exposure concerns farmers, breeders, animal feed workers, and veterinarians. |
|
Mechanism of action |
Tylosin is a 16-membered macrolide approved for therapy of a variety of infections in pigs, cattle, dogs, and poultry (see indications below). It is formulated as tylosin tartrate or tylosin phosphate. Like other macrolide antibiotics, tylosin inhibits bacteria by binding to the 50S ribosome and inhibiting protein synthesis. Spectrum of activity is limited primarily to gram-positive aerobic bacteria. Clostridium and Campylobacter are usually sensitive. The spectrum also includes the bacteria that cause BRD. Escherichia coli and Salmonella are resistant. In pigs, Lawsonia intracellularis is sensitive. |
|
Side effects |
Tylosin may cause diarrhea in some animals. However, oral treatment for colitis in dogs has been administered for several months with safety. Skin reactions have been observed in pigs. Oral administration to horses has been fatal. |
|
Safety Profile |
Poison by intravenous route. Moderately toxic by ingestion and intraperitoneal routes. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx. See also TnOSIN HYDROCHLORIDE. |
|
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments |
Although the injectable form of tylosin is approved for use in dogs and cats, it is rarely used parenterally in those species. Oral tylosin is sometimes recommended for the treatment of chronic colitis in small animals (see Doses), but controlled studies documenting its efficacy have not been performed. Tylosin is also used clinically in cattle and swine for infections caused by susceptible organisms. |
|
Solubility in organics |
soluble in lower alcohols, esters, ketones,chlorinated hydrocarbons, benzene, ether, chloroform. |
|
Definition |
ChEBI: A macrolide antibiotic that is tylonolide having mono- and diglycosyl moieties attached to two of its hydroxy groups. It is found naturally as a fermentation product of Streptomyces fradiae. |
|
Brand name |
Tylan (Lilly). |
|
Who Evaluation |
Evaluation year: 2008 |
-
The invention relates to a method for us...
An efficient method of protecting the 10...
Tylosin has been synthesized by regio- a...


desmycosin
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
|
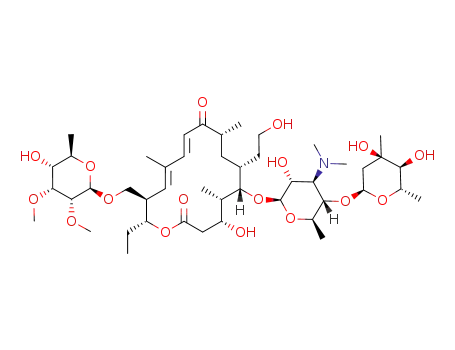
20-dihydrotylosin


tylosin
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With sodium hypochlorite; 2,2,6,6-Tetramethyl-1-piperidinyloxy free radical; sodium hydrogencarbonate; potassium bromide; In ethyl acetate; at 0 - 5 ℃; for 6h;
|
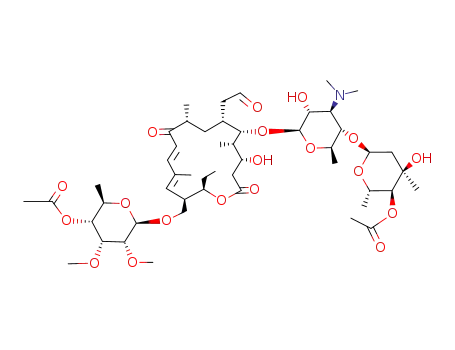
C50H81NO19
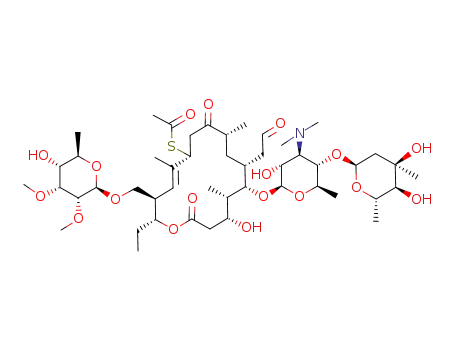
C48H81NO18S
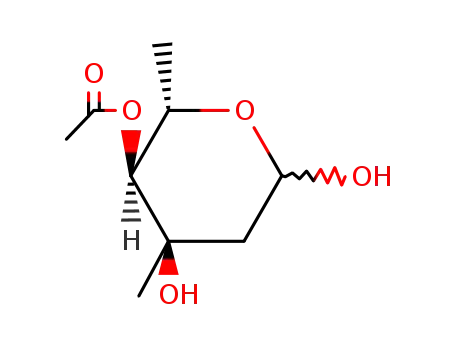
4-O-acetylmycarose
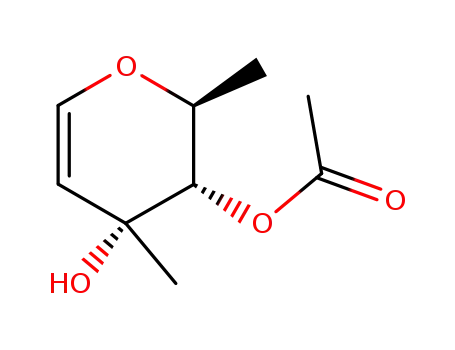
4-O-acetyl-1,5-anhydro-2,6-dideoxy-3-C-methyl-L-ribo-hex-1-enitol
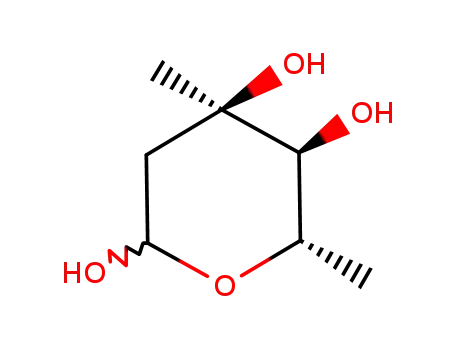
2,4,6-trideoxy-3-methyl-α,β-L-ribo-hexopyranose
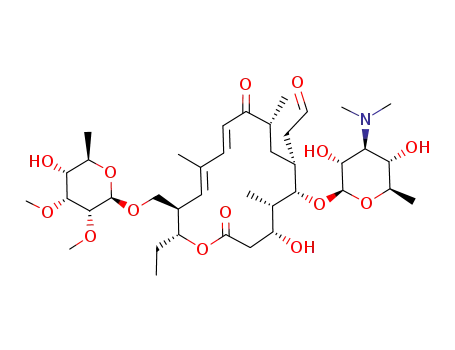
tylosin B

20-dihydrotylosin
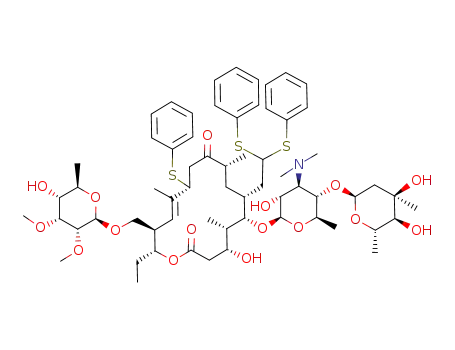
(11R)-20-deoxo-10,11-dihydro-11-phenylthiotylosin 20-diphenylthioacetal