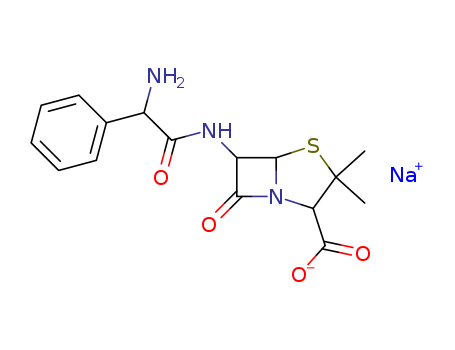

CasNo: 69-52-3
MF: C16H18N3NaO4S
Appearance: White powder
|
Broad-spectrum penicillin |
Ampicillin sodium is a broad-spectrum penicillin, its antibacterial spectrum is broader than penicillin , it has antibacterial activity on some gram-negative bacteria (such as Haemophilus influenzae, Escherichia coli, Proteus mirabilis) . Its effects on gram-positive cocci are similar to penicillin. Enzymatic hydrolysis of penicillin produced by bacteria may also make it inactive. It is clinically applicable in the treatment of respiratory infections, urinary tract infections, gastrointestinal tract infections, skin and soft tissue infections, meningitis, septicemia, endocarditis caused by sensitive bacteria. This product is a drug of choice for enterococcal infections. The above information is edited by the lookchem of Tian Ye. |
|
production method |
It is derived from the ampicillin salifying : Ampicillin is suspended in water, adjust to pH 9 with sodium hydroxide solution, dissolve and filter . The filtrate is added active carbon, and is filtered and the filtrate is dried at a low temperature, to obtain the product. |
|
Toxicity grading |
Low toxic |
|
Acute toxicity |
Oral-rat LD50:> 5314 mg/kg; Oral-Mouse LD50:> 5314 mg/kg. |
|
Flammability and hazard characteristics |
Combustion produces toxic sodium oxide, nitrogen oxide and sulfur oxide gases. |
|
Storage Characteristics |
Ventilated, low-temperature ,dry storeroom. |
|
Extinguishing agent |
Water, dry powder, foam, sand. |
|
Biological Activity |
ampicillin sodium is a competitive inhibitor of the enzyme transpeptidase with ic50 value of 1.8 μg/ml [1].ampicillin is a β-lactam antibiotic that kills bacteria by inhibiting transpeptidase reactions. transpeptidase is involved in the final stages of cell wall biosynthesis and inhibition of it ultimately leads to cell lysis [1].in e. coli 146 cells treated with ether, ampicillin showed no significant inhibition on the transpeptidase reaction at concentrations below 0.5 μg/ml, but exhibited 50% inhibition at the concentration of 1.8 μg/ml. in e. coli 146 cells, the minimal inhibitory concentration (mic) of ampicillin was 3.1 μg/ml [1]. in e. coli and s. typhi, ampicillin and epicillin at concentrations close to mic values killed bacteria at slower rates than amoxycillin [2].in experimental mouse infections, oral or subcutaneous treatment of ampicillin at the dose of 0.2 ml/20 g was significantly more effective than epicillin and amoxycillin against the majority of infections [2].[1]. moore b a, jevons s, brammer k w. inhibition of transpeptidase activity in escherichia coli by thienamycin. antimicrobial agents and chemotherapy, 1979, 15(6): 831-833.[2]. basker m j, gwynn m n, white a r. comparative activities of ampicillin, epicillin and amoxycillin in vitro and in vivo. chemotherapy, 1979, 25(3): 170-180. |
|
Biochem/physiol Actions |
Mode of Action: This is a ?-lactam antibiotic that inhibits bacterial cell-wall synthesis by inactivating transpeptidases on the inner surface of the bacterial cell membrane. Mode of Resistance: Administration with ?-lactamase cleaves the ?-lactam ring of Ampicillin and inactivates it. Antimicrobial Spectrum: Includes both gram-positive (similar to benzylpenicillin) and gram-negative bacteria (similar to tetracyclines and chloramphenicol. |
|
Contact allergens |
Ampicillin caused contact dermatitis in a nurse also sensitized to amoxicillin (with tolerance to oral phenoxymethylpenicillin) and in a pharmaceutical factory worker. Systemic drug reactions are common. Crossreactivity is regular with ampicillin and can occur with other penicillins. |
|
Safety Profile |
Moderately toxic by intraperitoneal route. Human systemic effects by ingestion: hypermotility, diarrhea, and other gastrointestinal changes. Questionable carcinogen. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of NOx, Na2O, and SOx. |
|
Category |
Toxic substances |
|
Brand name |
Polycillin-N (Bristol-Myers Squibb). |
|
General Description |
Chemical structure: ?-lactam |
InChI:InChI=1/C16H19N3O4S.Na/c1-16(2)11(15(22)23)19-13(21)10(14(19)24-16)18-12(20)9(17)8-6-4-3-5-7-8;/h3-7,9-11,14H,17H2,1-2H3,(H,18,20)(H,22,23);/q;+1/t9-,10-,11+,14-;/m1./s1
The present invention discloses an ampic...
The invention discloses a method for pre...
-
In the process for preparing an organic ...
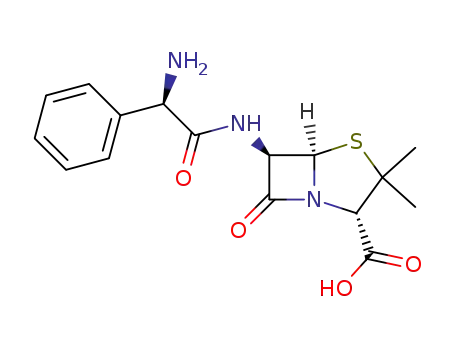
ampicillin

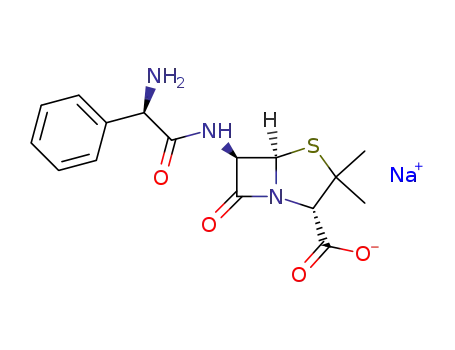
ampicillin sodium salt
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
ampicillin; With triethylamine; In acetone; at 0 - 5 ℃;
With sodium acetate; sodium hydrogencarbonate; In acetone; at 0 - 15 ℃;
|
|
|
With diisopropylamine; sodium 2-ethylhexanoic acid; In methanol; dichloromethane; at 15 ℃; Large scale;
|
76.5 kg |


ampicillin sodium salt
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
|
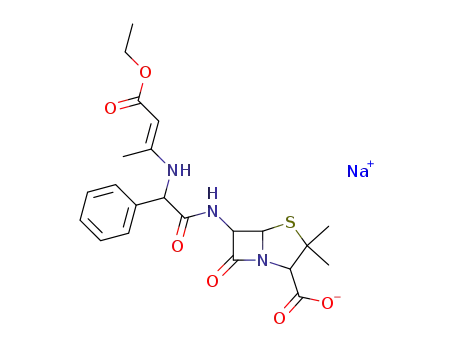
N-(1-methyl-2-ethoxycarbonylvinyl)ampicillin sodium

ampicillin

N-(1-methyl-2-ethoxycarbonylvinyl)ampicillin sodium
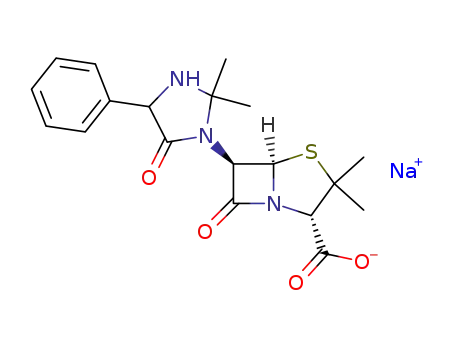
Sodium; (2S,5R,6R)-6-(2,2-dimethyl-5-oxo-4-phenyl-imidazolidin-1-yl)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-aza-bicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylate
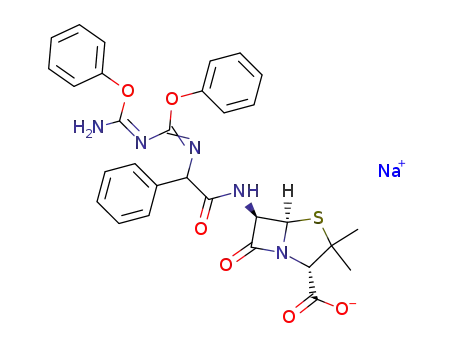
C30H28N5O6S(1-)*Na(1+)
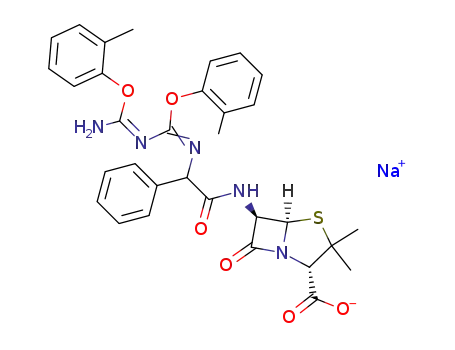
C32H32N5O6S(1-)*Na(1+)