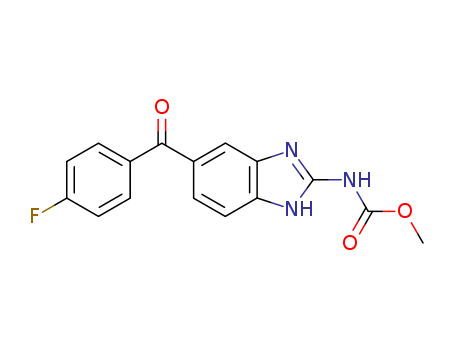

CasNo: 31430-15-6
MF: C16H12FN3O3
Appearance: almost white powder
|
Manufacturing Process |
To a stirred and cooled (ice bath) suspension of 25 parts of aluminum chloride in 52 parts of fluorobenzene is added dropwise a solution of 27.5 parts of 4- chloro-3-nitrobenzoyl chloride in 52 parts of fluorobenzene. Upon completion, stirring is continued overnight at room temperature. The reaction mixture is poured onto water and the product is extracted with methylene chloride. The extract is washed successively with sodium hydrogen carbonate solution and water, dried, filtered and evaporated in vacuo. The solid residue is crystallized from 2-propanol, yielding 4-chloro-4'-fluoro-3-nitrobenzophenone; MP 97.9°C.A mixture of 24.5 parts of 4-chloro-4'-fluoro-3-nitrobenzophenone, 72 parts of methanol, 13 parts of sulfolane and 3.12 parts of ammonia is heated in a sealed tube for 20 hours at 120°C. To the reaction mixture is added successively 50 parts of water and 25 parts of a diluted hydrochloric acid solution and the whole is stirred and refluxed for 5 minutes. The reaction mixture is cooled and the precipitated product is filtered off. It is washed with 2-propanol and recrystallized from 640 parts of toluene, yielding 4-amino-4'- fluoro-3-nitrobenzophenone; MP 199°C.A mixture of 14.5 parts of 4-amino-4'-fluoro-3-nitrobenzophenone, 160 parts of methanol, 6 parts of concentrated hydrochloric acid solution and 0.5 part of platinum oxide is hydrogenated at normal pressure and at room temperature. After the calculated amount of hydrogen is taken up, hydrogenation is stopped. The catalyst is filtered off and the filtrate is evaporated. The residue is washed with 2-propanol and dried, yielding 3,4-diamino-4'- fluorobenzophenone hydrochloride; MP 226°C to 230.5°C.A mixture of 89 parts of S-methylisothiourea sulfate, 6.05 parts of methyl chloroformate in 7 parts of water is cooled, and at a temperature of 5°C to 10°C, sodium hydroxide solution 25% is added until pH equals 8. Then there are added successively 6.4 parts of acetic acid, 2.6 parts of sodium acetate and 8.9 parts of 3,4-diamino-4'-fluorobenzophenone hydrochloride and the whole is stirred while heating at 85°C for 45 minutes (during this reaction time, water and 2-propanol is added). The precipitated product is filtered off, washed with methanol and recrystallized from a mixture of 200 parts of acetic acid and 80 parts of methanol, yielding methyl N-[5(6)-p-fluorobenzoyl-2- benzimidazolyl] carbamate; MP > 260°C. |
|
Therapeutic Function |
Anthelmintic |
|
Biochem/physiol Actions |
Flubendazole, an antithelmintic, has been widely used in treating intestinal parasites. Additionally, Flubendazole has been reported to exert anticancer activities. |
|
Definition |
ChEBI: A member of the class of mebendazole in which the benzoyl group is replaced by a p-fluorobenzoyl group. A broad-spectrum anthelmintic, it is used, particularly in veterinary medicine, for the treatment of nematodal infections. |
|
General Description |
Flubendazol is a broad spectrum anthelmintic, which belongs to the class of compounds known as benzimidazoles. It can be widely used in veterinary and human medicine. It mainly finds applications in deworming poultry, swine, dogs and cats. |
InChI:InChI=1/C16H12FN3O3/c1-23-16(22)20-15-18-12-7-4-10(8-13(12)19-15)14(21)9-2-5-11(17)6-3-9/h2-8H,1H3,(H2,18,19,20,22)
The invention relates to a synthesis met...
The invention relates to a preparation m...
The present invention is directed to the...
A series of alkyl-(5-acyl-l-H-benzimidaz...
(3,4-diaminophenyl)(4-fluorophenyl)ketone

O-methyl-N-(methoxycarbonyl)-isourea

flubendazole
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With formic acid; at 80 ℃; for 3h;
|
87.6% |
C16H15FN4O3

flubendazole
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With formic acid;
|
(3,4-diaminophenyl)(4-fluorophenyl)ketone
O-methyl-N-(methoxycarbonyl)-isourea
4-chloro-3-nitrobenzoate
4-chloro-3-nitro-benzoyl chloride
C17H15FN3O7P
C17H15FN3O7P