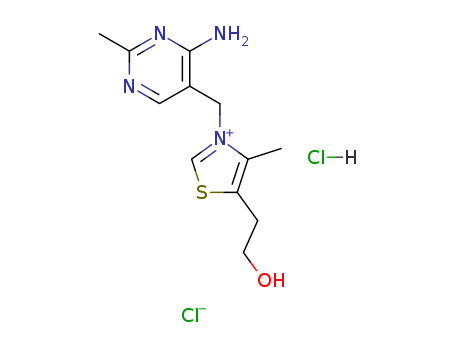

CasNo: 67-03-8
MF: C12H17ClN4OS.HCl
Appearance: White crystalline powder
|
Preparation |
By linking the preformed thiazole and pyrimidine ring system. |
|
Health Hazard |
Diseases and disorders resulting from a deficiency of thiamine include beriberi, opisthotonos (in birds), polyneuritis, hyperesthesia, bradycardia, and edema. Rather than a specific disease, beriberi may be described as a clinical state resulting from a thiamine deficiency. In body cells, thiamine pyrophosphate is required for removing carbon dioxide from various substances, including pyruvic acid. |
|
Biochem/physiol Actions |
Thiamine is an essential coenzyme in carbohydrate metabolism. Deficiency of thiamine causes beriberi, a neurological and cardiovascular disease. Thiamine is administered in case of deficiency, either due to reduced intake or synthesis. Congenital defect in the thiamine transporter gene SLC19A2 causes thiamine-responsive megaloblastic anemia syndrome (TRMA). Thiamine mimics acetylcholine in brain and possible exerts a role in Alzheimer′s disease. Thiamine deficiency in ruminants causes polioencephalomalacia. |
|
Safety Profile |
Poison by intravenous and intraperitoneal routes. Mildly toxic by ingestion. The vitamin is destroyed by alkalies and alkaline drugs such as phenobarbital sodium and by oxidzing and reducing agents. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of HCl, Cl-, SOx, and NOx. |
|
Environmental Fate |
Thiamine and its common phosphate analogs are readily soluble in water and ubiquitously utilized in nature. |
|
Purification Methods |
The hydrochloride crystallises from 95% EtOH (solubility is ca 1%). The monohydrate is dehydrated at 100o in vacuo over H2SO4, but is hygroscopic and picks up one molecule of H2O readily. It can be sterilised at 100o if the pH of the solution is below 5.5. The nitrate has m 196-200o(dec) and is more stable than the hydrochloride. The picrolonate crystallises from H2O and is dimorphic, m 164-165o and 228-229o(dec). [Todd & Bergel J Chem Soc 364, 367 1937, J Am Chem Soc 58 1063, 1504 1936, 59 526 1937, Beilstein 27 IV 1766.] |
|
Definition |
ChEBI: A hydrochloride obtained by combining thiamine chloride with one molar equivalent of hydrochloric acid. |
|
General Description |
Thiamine is a water-soluble vitamin of the B complex whose phosphate derivatives are involved in many cellular processes required for overall human health. Thiamine deficiency, often the result of impaired nutritional status associated with chronic diseases from alcoholism to HIV-AIDS, is monitored in patient whole blood samples by HPLC. |
|
Who Evaluation |
Evaluation year: 2002 |
InChI:InChI=1/2C12H17N4OS.4ClH/c2*1-8-11(3-4-17)18-7-16(8)6-10-5-14-9(2)15-12(10)13;;;;/h2*5,7,17H,3-4,6H2,1-2H3,(H2,13,14,15);4*1H/q2*+1;;;;/p-4
-
-
The invention provides a synthetic proce...
Provided, among other things, is a metho...
A controlled release pharmaceutical prep...
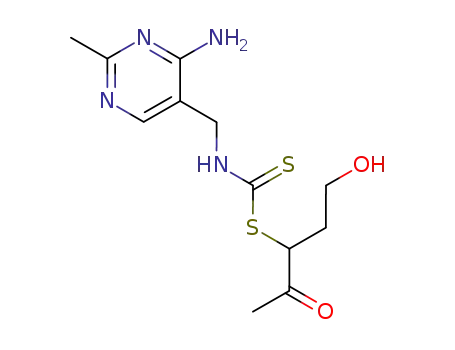
(4-amino-2-methyl-pyrimidin-5-ylmethyl)-dicarbothioamidoic acid-(1-acetyl-3-hydroxy-propyl ester)

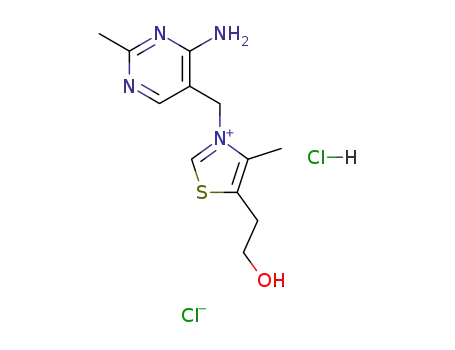
Thiamine hydrochloride
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
hydrogenchloride; dihydrogen peroxide;
In
water;
at -10 ℃;
for 20h;
|
94.7% |
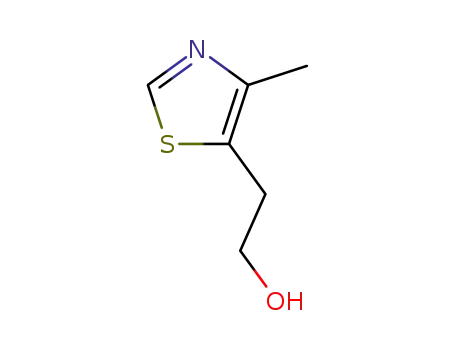
5-hydroxyethyl-4-methylthiazole
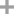
5-ethoxymethyl-2-methyl-pyrimidin-4-ylamine


Thiamine hydrochloride
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
5-ethoxymethyl-2-methyl-pyrimidin-4-ylamine;
With
hydrogenchloride;
In
water;
at 90 - 95 ℃;
for 5h;
5-hydroxyethyl-4-methylthiazole;
at 102 ℃;
for 4h;
|
0.85 g |
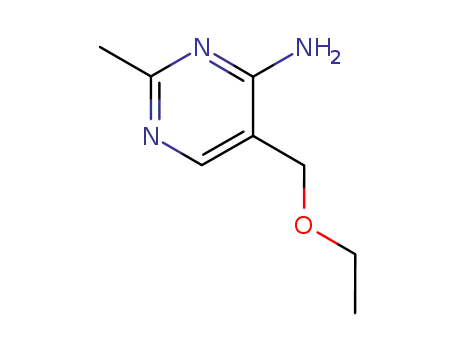
4-Amino-2-methyl-5-thioformamidomethylpyrimidin
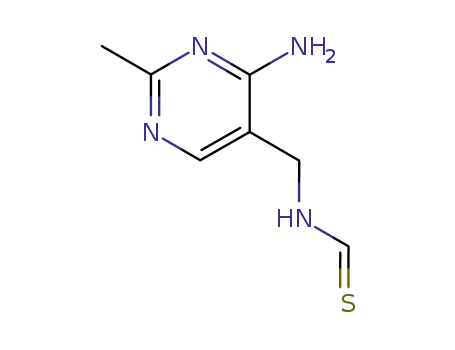
5-Acetoxy-3-chloropentan-2-one
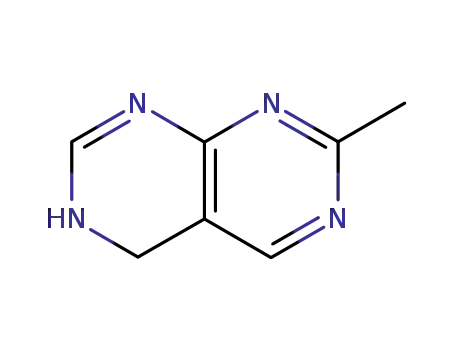
3,4-Dihydro-7-methylpyrimido<4,5-d>pyrimidine
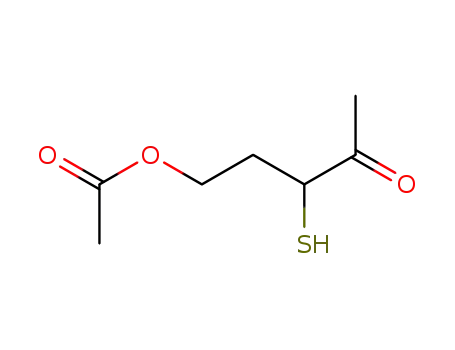
3-Mercapto-4-oxopentyl Acetate
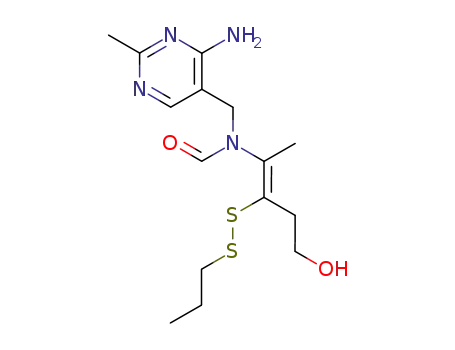
thiamine propyl disulfide
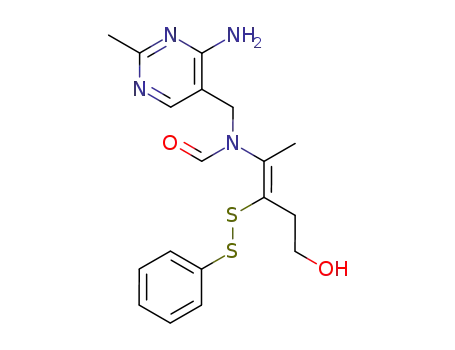
N-(4-amino-2-methyl-pyrimidin-5-ylmethyl)-N-(4-hydroxy-1-methyl-2-phenyldisulfanyl-but-1-enyl)-formamide
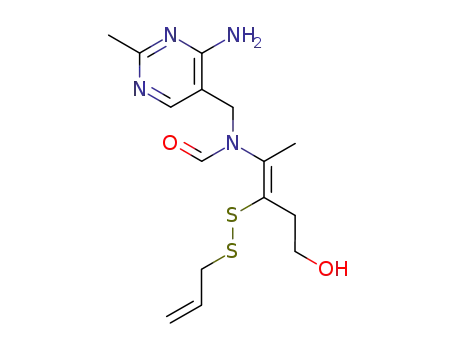
N-(2-allyldisulfanyl-4-hydroxy-1-methyl-but-1-en-t-yl)-N-(4-amino-2-methyl-pyrimidin-5-ylmethyl)-formamide
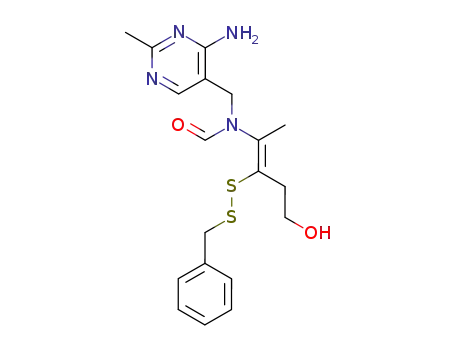
N-(4-amino-2-methyl-pyrimidin-5-ylmethyl)-N-(2-benzyldisulfanyl-4-hydroxy-1-methyl-but-1-enyl)-formamide