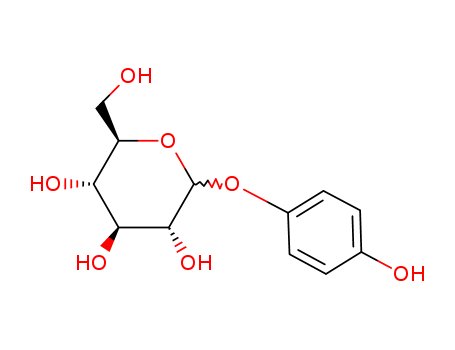

CasNo: 84380-01-8
MF: C12H16O7
Appearance: White Crystalline powder
|
benefits |
Ensures an even skin tone after only one month;Reduces the degree of skin tanning after UV exposure;Helps to minimize the appearance of liver spots. |
|
Biological Functions |
Alpha arbutin acts as a tyrosinase competitive inhibitor and also slows melanosome maturation (the organelles that synthesize and store melanin or pigment).3 This is significant because it works on two different mechanisms of pigmentation. Melanin is derived from the amino acid tyrosine and this conversion is regulated by the enzyme tyrosinase. Alpha arbutin is similar in structure to tyrosine, which fits into tyrosinase, needed for melanogenesis. This means that alpha arbutin is reversibly competing with tyrosine for a spot on the enzyme and not inhibiting cell viability, so therefore is not cytotoxic. By targeting tyrosinase, the rate-limiting enzyme in melanin formation, as well as slowing production of the organelles that produce melanin, alpha arbutin is a potent skin brightening agent. |
|
Mechanism of action |
Alpha arbutin is frequently marketed as a safer alternative to hydroquinone (a popular skin-lightening ingredient that has been banned in Europe and Australia). It has similar results in brightening skin but without the dangerous bleaching process. Instead, it reduces skin’s pigment production by suppressing the enzymes that stimulate melanin. This also slows down the process by which UV light causes pigmentation, so it both prevents and treats pigmentation issues. |
|
Synthesis |
In a 100 ml reaction flask, add (1.21 g, 2.5 mmol)P-acetoxyphenyl-2,3,4,6-tetra-O-acetyl-β-D-glucopyranoside 6,Add 36 ml of anhydrous methanol to dissolve, magnetically stir, add a catalytic amount of 0.06 g of sodium methoxide, react at 25 ° C for 2 hours, add acidic resin to neutralize to system pH = 7,The resin was recovered by filtration, and the filtrate was concentrated to dryness under reduced pressure.Beta-arbutinWhite solid 0.65 g,The yield was 96%. |
|
|
|
|
Definition |
Alpha arbutin, also called Hydroquinone β-D-glucopyranoside, is a naturally occurring antioxidant and skin brightener that is naturally found in the bearberry plant. It reduces melanin formation, improving the appearance of age spots, freckles, melasma, and post-inflammatory pigmentation. |
|
General Description |
α-Arbutin is a glycosylated hydroquinone and an anomer of naturally occurring arbutin. It is a potent inhibitor of tyrosinase, a vital enzyme involved in epidermal melanin biosynthesis. α-Arbutin finds extensive application as a powerful skin-lightening agent in cosmetic industries. |
InChI:InChI=1/C12H16O7/c13-5-8-9(15)10(16)11(17)12(19-8)18-7-3-1-6(14)2-4-7/h1-4,8-17H,5H2/t8-,9-,10+,11-,12+/m1/s1
The invention provides a chemical synthe...
The invention provides a method for prep...
Although numerous biologically active mo...
Thanks to its broad acceptor specificity...
D-glucose

hydroquinone

arbutin

4-hydroxyphenyl α-D-glucopyranoside
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With toluene-4-sulfonic acid; In dimethyl sulfoxide; at 100 ℃; for 10h;
|
11% 4% |
O-p-acetoxyphenyl-2,3,4,6-tetra-O-acetyl-β-D-glucose

4-hydroxyphenyl α-D-glucopyranoside
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With methanol; sodium methylate; at 25 ℃; for 2h; Temperature;
|
96% |
D-glucose
hydroquinone
Sucrose
maltopentaose
O-p-acetoxyphenyl-2,3,4,6-tetra-O-acetyl-β-D-glucose